
PUBLICATIONS

Genetic and pharmacologic modulation of cementogenesis via pyrophosphate regulators
July 2020, Bone
Authors:
Chu EY, Vo TD, Chavez MB, Nagasaki A, Mertz EL, Nociti FH, Aitken SF, Kavanagh D, Zimmerman K, Li X, Stabach PR, Braddock DT, Millan JL, Foster BL, Somerman MJ.
Synopsis:
Pyrophosphate (PPi) is a major source of control of mineralization in biological settings and in particular with cementum; thereby having a large role in tooth attachment. The study uses several genetic and pharmacologic modulation of PPi to provide insights into cementum formation.

Dental and craniofacial defects in the Crtap-/- mouse model of osteogenesis imperfecta type VII
March 2020, Developmental Dynamics
Authors:
Xu H, Lenhart SA, Chu EY, Chavez MB, Wimer HF, Dimori M, Somerman MJ, Morello R, Foster BL, Hatch NE.
Synopsis:
Crtap knockout mice exhibited severe dental and craniofacial abnormalities that mirror osteogenisis imperfecta type VII in humans with mutations in CRTAP implying the use of Crtap knockout mice as a good model to study OI type VII.

Dentoalveolar Defects in the Hyp Mouse Model of X-linked Hypophosphatemia.
January 2020, Journal of Dental Research
Authors:
Zhang H, Chavez MB, Kolli TN, Tan MH, Fong H, Chu EY, Li Y, Ren X, Watanabe K, Kim DG, Foster BL.
Synopsis:
Hyp mice are an established model for XLH. This study examined in detail the dentoalvolar defects in Hyp mice and used high reslolution micro-CT and nanoindentation to examine the perilacular densities of cementocytes, leading the way for future studies to examine how treatments effect these defects.

Loss of Discoidin Domain Receptor 1 Predisposes Mice to Periodontal Breakdown
October 2019, Journal of Dental Research
Authors:
Chavez MB, Kolli TN, Tan MH, Zachariadou C, Wang C, Embree MC, Lira Dos Santos EJ, Nociti FH Jr, Wang Y, Tatakis DN, Agarwal G, Foster BL.
Synopsis:
Mice lacking Discoidin Domain Receptor 1 (DDR1) although developed a healthy periodontium into early adulthood spontaneously developed bacterial associated inflammatory bone loss consistent with periodontitis in mid to latter adulthood.

Inactivating Mutation in IRF8 Promotes Osteoclast Transcriptional Programs and Increases Susceptibility to Tooth Root Resorption.
October 2019, Journal of Bone and Mineral Research
Authors:
Thumbigere-Math V, Foster BL, Bachu M, Yoshii H, Brooks S, Chavez MB, Coulter A, Togi S, Neely AL, Deng Z, Mansky KC, Ozato K, Somerman MJ.
Synopsis:
In this study for the first time to our knowledge we reported idiopathic root resorption associated with a novel mutation in interferon regulatory factor 8 (IRF8 G388S) a type of periodontal disease and compared to IRF8 knockout-mice with emphasis on osteoclast regulation.
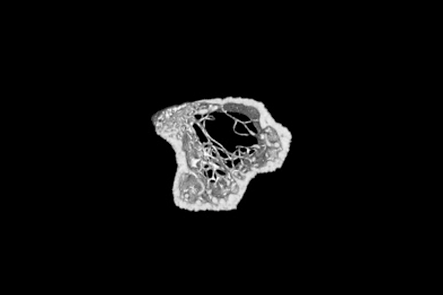
Antibiotic Perturbation of Gut Microbiota Dysregulates Osteoimmune Cross Talk in Postpubertal Skeletal Development.
February 2019, The American Journal of Pathology
Authors:
Hathaway-Schrader JD, Steinkamp HM, Chavez MB, Poulides NA, Kirkpatrick JE, Chew ME, Huang E, Alekseyenko AV, Aguirre JI, Novince CM.
Synopsis:
Mice being administered broad spectrum antibiotics for 6 weeks had adverse effects on bone metabolism due to dysregulation of signaling from gut microbiota ablated by antibiotics

Genetic engineering a large animal model of human hypophosphatasia in sheep.
November 2018, Scientific Reports
Authors:
Williams DK, Pinzón C, Huggins S, Pryor JH, Falck A, Herman F, Oldeschulte J, Chavez MB, Foster BL, White SH, Westhusin ME, Suva LJ, Long CR, Gaddy D.
Synopsis:
For the first time a genetic mutated sheep model for hypophosphatasia (HPP) was engineered based on known human mutatoins. The sheep phenocopied the human condition showing this model as a good model for human HPP

Reduced orthodontic tooth movement in Enpp1 mutant mice with hypercementosis.
March 2018, Journal of Dental Research
Authors:
Wolf M, Ao M, Chavez MB, Kolli TN, Thumbigere-Math V, Becker K, Chu EY, Jäger A, Somerman MJ, Foster BL.
Synopsis:
Enpp1 knockout mice exhibited significant reduction in orthodontic tooth movement induced by orthodontic wire compared to controls. Human patients with mutations in ENPP1 also report reduced tooth movement under orthodontic treatment. Our evidence points to hypercementosis associated with these mutations to be the culprit.

Tristetraprolin Is Required for Alveolar Bone Homeostasis.
July 2018, Journal of Dental Research
Authors:
Steinkamp HM*, Hathaway-Schrader JD*, Chavez MB, Aartun JD, Zhang L, Jensen T, Shojaee Bakhtiari A, Helke KL, Stumpo DJ, Alekseyenko AV, Novince CM, Blackshear PJ, Kirkwood KL.
Synopsis:
Tristetraprolin (TTP) is an RNA-binding protein that is responsible for targeting several immunomodulatory mRNA strands for degradation. In TTP knock-out mice this lack of control causes a massive run away auto-inflammatory state and causes severe alveolar bone loss

MMP20 overexpression disrupts molar ameloblast polarity and migration.
July 2018, Journal of Dental Research
Authors:
Shin M, Chavez MB, Ikeda A, Foster BL, Bartlett JD.
Synopsis:
MMP20 a key enamel protein that is responsible for cleaving enamel proteins during the secretory stage of amelogenisis was over expressed in the mice in this study. This resulted in a dramatic amelogenisis imperfecta phenotype, evidence points to premature degradation of ameloblastin.

Osteopontin regulates dentin and alveolar bone development and mineralization.
February 2018, Bone
Authors:
Foster BL, Ao M, Salmon CR, Chavez MB, Kolli TN, Tran AB, Chu EY, Kantovitz KR, Yadav M, Narisawa S, Millán JL, Nociti FH, Somerman MJ.
Synopsis:
Osteopontin knockout mice exhibited alveolar bone and dentin defects compared to WT controls. However, OPN was did not alter acellular cementum and a double knockout of OPN and ANK did not exacerbate the hypercementosis seen in ANK knockout mice.


Hypercementosis Associated with Enpp1 Mutations and GACI
April 2018, Journal of Dental Research
Authors:
Thumbigere-Math V, Alqadi A, Chalmers NI, Chavez MB, Chu EY, Collins MT, Ferreira CR, FitzGerald K, Gafni RI, Gahl WA, Hsu KS, Ramnitz MS, Somerman MJ, Ziegler SG, Foster BL.
Synopsis:
In 6 patients with ENPP1 mutations all exhibited mineralziation defects with a large effect on cementum, 4-fold increase in accelluar cementum thickness. This phenotype was consistent with a mouse model lacking Enpp1.

Overlapping functions of bone sialoprotein and pyrophosphate regulators in directing cementogenesis.
December 2017, Bone
Authors:
Ao M, Chavez MB, Chu EY, Hemstreet KC, Yin Y, Yadav MC, Millán JL, Fisher LW, Goldberg HA, Somerman MJ, Foster BL.
Synopsis:
Bone sialoprotein (BSP) and progressive ankylosis (ANK) both play important roles in cementogenisis. BSP KO mice exhibit a lack of cementum while ANK KO mice exhibit hypercementosis. When the mice were crossed to be BSP & ANK knockouts cementum formed suggesting phosphate regulators play a larger role in cementum formation than BSP.

Commensal Gut Microbiota Immunomodulatory Actions in Bone Marrow and Liver have Catabolic Effects on Skeletal Homeostasis in Health.
July 2017, Scientific Reports
Authors:
Novince CM, Whittow CR, Aartun JD, Hathaway JD, Poulides N, Chavez MB, Steinkamp HM, Kirkwood KA, Huang E, Westwater C, Kirkwood KL.
Synopsis:
Mice lacking any microbiota had altered effects on bone metabolism controlled through the gut's ability to use immunomodulatory signals.

Sex-based Differential Regulation of Bacterial-induced Bone Resorption.
June 2017, Journal of Periodontal Research
Authors:
M.S Valerio, D.S. Basilakos, J.E. Kirkpatrick, M. Chavez, J. Hathaway-Schrader, B.A. Herbert, K.L. Kirkwood.
Synopsis:
In a mouse model for alveolar bone loss, we observed sexual dymorphism in regards to immune response supporting observations seen in humans.

